What is Tunnel Engineering and Tunnel Design? 7 Important Points
- By
- Pooja |
- September 04, 2021 |
- Civil Engineering, Tunnel Engineering,
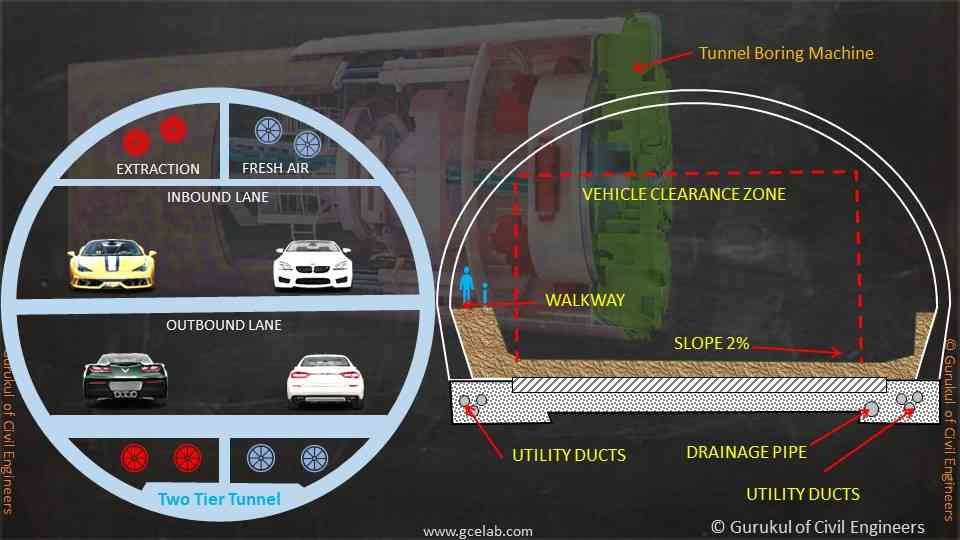
Table of Contents
What is the purpose of the Tunnel?
What is the well-known tunnel design Software?
What are the methods of Tunneling?
Shaft Method of Tunnel Construction
What are the different types of tunnels?
What is Tunnel Engineering?
Underground construction and tunnel engineering are genuinely interdisciplinary processes, requiring knowledge and skills from civil engineering, geological engineering, and mining engineering, as well as mechanical engineering, geophysics, electrical engineering, geology, etc.
Students must learn to design, build, rehabilitate, and maintain structures peculiar to the underground space, and the use of tunnels for commercial, transportation, water, wastewater, and utility, etc in addition to typical construction procedures.
What is the purpose of the Tunnel?
Tunnels are passages beneath the ground that are utilized for transportation. They might be used to transport freight and passengers, as well as water and sewage. Beyond a certain depth, tunnels are more cost-effective than open cuttings. During the construction stage, tunnels normally undisturbed the surface activities like live traffic, open recreational activities, etc.
Tunnels are considered to be less expensive than bridges or open steep earthwork cuttings for highway projects or transporting public utility services such as water and wastewater or gas line. The inability of these structures to be built out of natural resources such as rock and soil leads to their failure.
Geological factors are expected to play a significant effect on their long-term stability. Aspects that are extremely important are such as ground and sub-ground conditions, construction sequencing, construction period, construction cost, etc. All these factors play a very important role in determining the feasibility of a tunnel project.
Read More:
What is Earthquake Resistant Building | Structure? 8 Important Points
What is the Function of Bridge Foundation or Pier and its Types? 5 Important Points
What is Tunnel design?
Accepting the inherent ambiguity linked with subterranean conditions that can be defined but never really known is a prerequisite for the tunnel design and construction process.
A typical tunnel project starts from the exploration of suitable ground conditions and then testing the engineering parameters, then moves to the selection process of tunnel excavation methods, then moves to the development of liner design parameters, and estimating surface settlements, and finally covers their effects on adjacent structures.
It uses various case studies of successfully executed completed projects to frame out the risks and mitigation strategies, lesson learned activities for the proposed project.
What is the well-known tunnel design Software?
- Tunnel Design Software
- PLAXIS3D tunnel software
- Flac3D
What are the methods of Tunneling?
Cut and Cover Method
Shallow tunnels are often built using the cut and cover method of tunnel construction. This approach involves excavating a trench in the ground and covering it with support capable of supporting the load. There are two methods for the cut and cover method. One is the bottom-up method, in which a tunnel is excavated beneath the surface and supported by the ground.
Another way is the top-down method, in which the side support walls are built first, either via slurry walling or contiguous bored piling. The roof is then installed on top of the walls, and excavation is completed. Finally, the base slab is built. The majority of underground metro rail stations are built utilizing the cut-and-cover approach.
Bored Tunnel Method
The method of using a bored tunnel is cutting-edge expertise. Tunnel boring machines are used for this method, which works automatically and makes the entire tunnelling procedure easier. It is also a more efficient and effective way of tunnel construction in urban, heavy trafficked locations where traffic diversion, and traffic management during construction is a highly difficult and expensive task.
Tunnel boring machines (TBMs) come in a variety of shapes and sizes to meet various ground conditions. These machines can work in challenging environments, such as below the water table. TBM can work in below-water-table circumstances because of a specific pressurized container.
Clay Kicking Method
This procedure is utilized when there is a lot of clay in the soil. This is a traditional approach that is still used for little jobs such as installing sewage pipes. In this procedure, a hole is dug into the earth, and then a depth tunnel is constructed by the clay kicker, which is mounted on a plank at a 450 angle. Under the clay kicker foot, there is a digging tool.
This is well-known since it was the method employed by Englishmen during World War I to bury mines.
Read More:
How to learn STAAD Pro? 7 Important Points
How do you answer tell me about yourself in an interview? 5 Important Points
Shaft Method of Tunnel Construction
In this method, the tunnel is constructed at a greater depth from the ground surface. The shaft is placed to a depth where the tunnel is required. The shaft is a long-term construction that works well with concrete walls. TBMs are deployed to excavate tunnels to the appropriate depth.
Tunnels have shafts at both ends. If the tunnel is excessively long, intermediate shafts are constructed. These shafts can be utilized for ventilation purposes and for emergency exits once the construction of the tunnel is completed.
Pipe Jacking Method
The pipe jacking method is recommended to build tunnels beneath existing facilities such as roads and railways. Hydraulic jacks are deployed to drive specifically designed pipes into the ground. Tunnels can have a maximum diameter of 3.2 meters.
What are the different types of tunnels?
Tunnels can be grouped into three main categories based on their intended use:
- Tunnels for traffic
- Tunnels for hydropower
- Tunnel for public utilities
Tunnel for traffic
Tunnels are constructed to transfer traffic load from surface to subsurface channels for a brief period of time in order to facilitate congestion-free traffic movements. Traffic tunnels are structures that allow traffic to move at a chosen pace, with optimum ease, and at a minimal cost.
There are three types of traffic tunnels:
- Railway tunnels,
- Highway tunnels, and
- Pedestrian tunnels.
Tunnel for Hydropower
These tunnels are constructed for hydropower generating, as the name suggests. They are hammered into rocks, allowing gravity to convey the water.
Tunnel for Public Utility
These tunnels are constructed for a specific function, such as the disposal of municipal trash, the transportation of pipelines, cables, and oil supplies, as well as water. In today's heavily populated cosmopolitan cities, they are also constructed for underground parking and storage.
Tunnel Engineering online courses Being a unique engineering discipline, Tunnel Engineering courses are expensive and are very few available in the market. Following are some well-known courses in Tunnel Engineering:
- Postgraduate course in Tunnel Engineering
- Certification course in Tunnel Engineering
- NPTEL course on Rock Mechanism
Gcelab.com also offers a unique Tunnel Engineering online course. The course covers various key aspects of Tunnel Engineering and assists the student to learn Tunnel Engineering and move forward in the right direction to make Tunnel engineering an aspiring career option.
I hope this blog offers you adequate information about Tunnel Engineering and Tunnel Design.
Please feel free to like, share and comment about it.
Admin, gcelab.com Please see our Pillar Post to know why we founded gcelab.com.
Read More:

Pooja
Founder at gcelab.com, Pooja is an Entrepreneur unlocking human potential. Working in the Principles of Lean Start-up, Pooja believes in Transparency and User Happiness the most. Pooja’s background in teaching gives her a sophisticated grasp on even the most tedious aspect of course building. She is passionate about people who believe that good is not enough.


