What is the Purpose of Underpinning the Foundation?
- By
- Pooja |
- July 21, 2022 |
- Civil Engineering, Innovation, Building/ Structure Engineering,
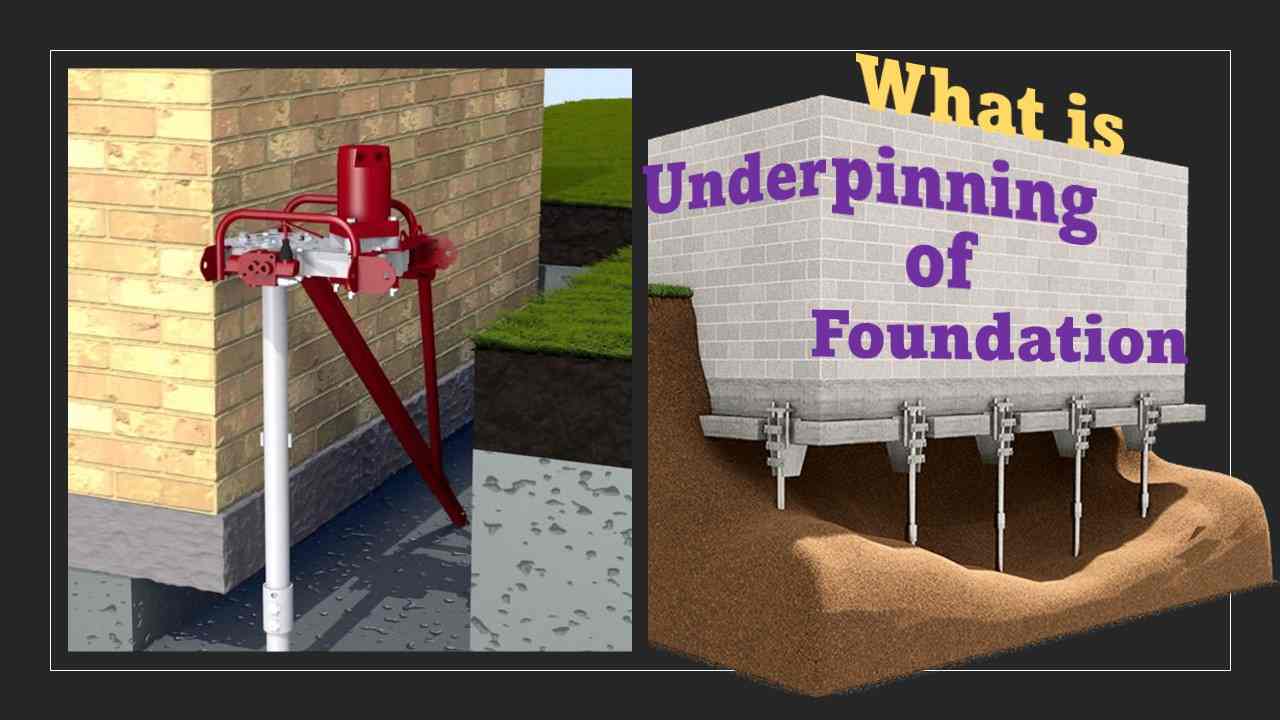
Table of Contents
Precautions to be taken in Pit Method
Pynford Stool Method of Underpinning
Structural Conditions that necessitate Underpinning
What is Underpinning?
Trying to stabilise and deepen an existing foundation by means of underpinning is a delicate building procedure that must be handled with care. A delicate repair like underpinning necessitates careful consideration of the many options.
Purpose of Underpinning
Underpinning is performed to meet the following purposes:
-
An existing shallow foundation can be brought up to a deeper depth when the adjacent building is erected with a deep foundation.
-
The addition of a basement to an existing building necessitates the installation of underpinning.
-
One of the key purposes of underpinning is to extend the depth of the current foundation (which is resting on weak strata) in order to place it on stronger strata of soil.
-
Because of cracks in the wall, the foundation of a building may become unstable.
Underpinning Methods
Following are the key methods of Underpinning:
Pit Method
A needle is put into a hole within the wall above the plinth level for each portion. The brickwork above the needle is backed by bearing plates to put on top of it. Wooden stands support it and they are tightened with screw jacks on both sides of the wall.
Precautions to be taken in Pit Method
The following points are important to remember while using the pit method:
- The round format is used for the alternating sections.
- The remainder of the portions can be tackled after that.
- When working on a long wall, it is best to begin at the centre and proceed outwards.
- Appropriate timbering of the foundation trench can be carried out for a deeper foundation.
- When a new foundation is strong enough, the needle beam can be removed.
- It is preferable to use concrete for the new foundation work.
- Cement mortar should be used to close the needle in the stonework.
Cantilever Beam Method:
Cantilever needle beams are considered in place of the central needle beam when the strong columns exist within the internal layout of the building or if the foundation is only being extended on one side.
Pile Method
Pile driving is done on both sides of the wall using this method. Concrete or steel needles pierce the walls to link the piles together. Additionally, these beams are utilised as pile toppers. Clayey soils and wet locations can benefit from this strategy. The load on the existing foundation has been greatly reduced.
Read More:
Underpinning to Walls:
For wall underpinning, the wall should be separated into bays and each bay should be treated individually to prevent the walls from fracturing, damaging, or settling.
- The leg and bay lengths are affected by the following factors:
- The total length of the wall is in metres.
- All of the dead and living fill the walls.
- The present foundation's capacity and soil type.
- Underpinning the wall is dependent on the structural integrity of the building's walls and foundation.
- Wall footing's capacity to spin and settle at varying rates of speed.
Jack Pile Underpinning
When traditional underpinning is prohibitively expensive due to the depth of sufficient bearing capacity in the subsoil, jack pile underpinning is recommended.
Pynford Stool Method of Underpinning
When the current foundation's soil has a low bearing capacity, Pynford underpinning is an appropriate type of underpinning because it allows the needle to go continuously to the walls.
The following are the specifics of the Pynford Stool Underpinning Technique:
- Sitting areas for steel or precast concrete stools are made in the wall.
- Over the aperture, stools were inserted and nailed to the soffit of the brickwork.
- The brickwork between the pined tools was removed to leave the wall supported on the pined stools.
- Fabricated and positioned bolstering around nailed stools.
- The construction of the moulds and the casting of the beams has been completed.
- After removing the formwork and allowing the beam to dry, it is fastened to the wall.
Root Pile or Angle Piling
Modern concrete drilling equipment is used in the root pile underpinning process in order to produce concrete that is both times- and cost-efficient. Because of the foregoing, this is a straightforward substitute for a more complex foundation”
Structural Conditions that necessitate Underpinning
Many factors lead an engineer to recommend an underlying approach for substructure stabilization, including Settlement that would occur if the decay of timber piles used as a foundation for regular constructions occurred. Water table changes are to blame for the decomposition of structures. A decline in the soil's bearing capacity can cause the structure to settle when the water table rises and falls. Settlement can occur if a structure is built on soil that lacks sufficient bearing capacity.
I hope this post provides you with a good understanding of the Underpinning of the Foundation and its associated features.
Please feel free to like, share and comment.
Admin, gcelab.com Please see our Pillar Post to know why we founded gcelab.com.
Read More:

Pooja
Founder at gcelab.com, Pooja is an Entrepreneur unlocking human potential. Working in the Principles of Lean Start-up, Pooja believes in Transparency and User Happiness the most. Pooja’s background in teaching gives her a sophisticated grasp on even the most tedious aspect of course building. She is passionate about people who believe that good is not enough.
Previous Post
What is Block Paving or Brick Paving?
Next Post


