What is Watershed Management?
- By
- Pooja |
- June 30, 2022 |
- Civil Engineering, Drainage Engineering, Innovation,
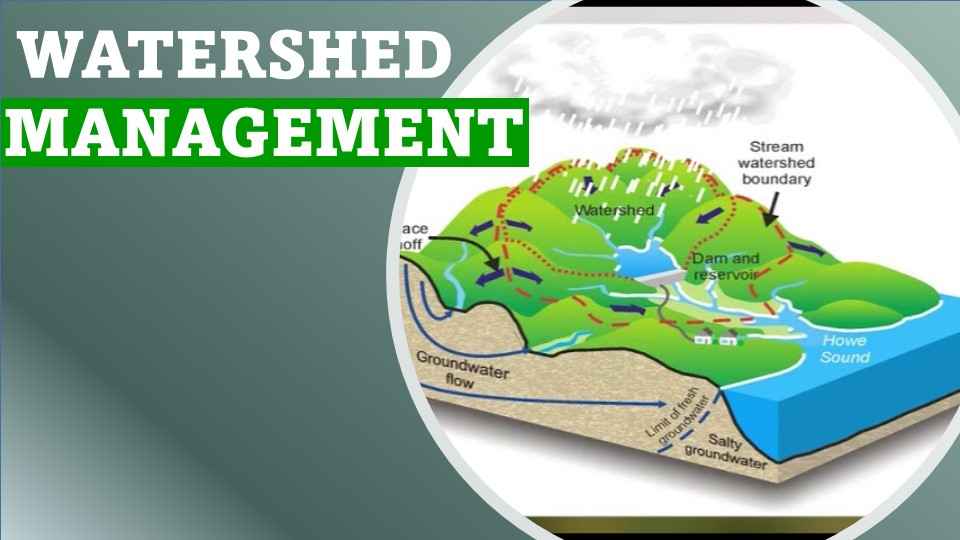
Table of Contents
Purpose of Watershed Management
Components of Watershed Management:
Water Management under the purview of Watershed Management:
Importance of Watershed Management
Concepts of Watershed Management
Practical Example of Watershed management
Recent Trends in Watershed Management
Latest Research on Watershed Management
What is Watershed Management
In order to conserve and enhance water quality and other natural resources, watershed management is implemented as a land-use strategy.
Purpose of Watershed Management
Strategy, analysis, and implementation are the main goals of watershed management.
Watershed management's primary goals and objectives are as follows:
- Approaching Land Degradation from a Multi-Facetted Approach in order to Maximize Production.
- Manage, control, and utilize water runoff.
- Optimize and sustain output while minimizing harm to natural resources and the environment by rationalizing land and water resource use.
- Solve the problem of soil erosion by ensuring optimal infiltration and percolation.
- As a way to limit sediment production on watersheds, reduce the impact of rain on soil and monitor its pace over time.
- Water resources need to be safeguarded and improved in tandem with flood mitigation and a reduction in the division of tanks and reservoirs.
- Increased irrigation and rainwater conservation for crops, as well as drought mitigation.
Components of Watershed Management:
Land Management:
When we talk about land management, we mean maintaining all of those aspects of the land that can potentially impact the soil's ability to produce food. Land management actions for watershed development must take into account the land's terrain, slope, formation, depth, texture, wetness, infiltration rate, and soil capabilities.
A wide range of land management initiatives includes the following:
- Plant-based measurements
- Measures pertaining to the structure
- Production metrics
- Safeguards for the home.
The principal means of land management is through the use of vegetative measures. There are several ways to manage land using vegetation, such as establishing grasslands and pastures, using contour farming and strip-cropping techniques on hillsides, or just keeping the ground covered with vegetation.
Farmers can use these strategies to prevent soil erosion at a lower cost and in a more convenient manner. Grassland management, agroforestry, mulching, vegetative hedges, and other similar activities are also included in this category.
Bundling, check dams, terracing, and other structural methods are employed to reduce soil loss in the steep terrain, particularly when vegetative procedures are inadequate. Because of the high costs involved, these procedures are not as frequent as vegetative measures.
Water Management under the purview of Watershed Management:
It's critical to keep an eye on the rainwater's flow in order to manage it. There are many ways to accomplish this, such as building a pond or reservoir in the area. Additionally, rain-dependent farming techniques can be used to better utilise rainwater as a water management measure. In addition to preserving rainwater, intelligent use of it for crop formation or similar farm operations is an important factor in water management.
As far as water management is involved, the range of the most appropriate irrigation method based on soil, crop, ground topography, water availability in the area, etc., is critical. Irrigation technologies with improved water use efficiency reduced water loss, and other advantages should always take precedence.
Water management can also be improved by selecting a suitable farming method, variety of crops, and harvest time based on water availability.
The following is a list of water management interventions:
- Harvesting rainwater.
- Recharge of the groundwater.
- Maintenance of a proper water-to-air ratio.
- water pollution prevention.
- efficient use of water resources.
Rainwater collection is the most important method of conserving water in a watershed. It is possible to store gathered rainwater for as long as it is required by planning and building the appropriate structures.
Rainwater collecting structures that are simple and affordable include, but are not limited to:
- Pits/tanks for percolation
- Ponds on farms
- Terraces and Bunds
Biomass Management:
The following areas of intervention in a watershed can help with biomass management:
- Conservation of the natural environment
- Regeneration of biomass
- Management and conservation of forest land
- Plant conservation and social forestry development
Steps of Watershed Management
Information regarding the watershed's land, water, soil, and vegetation problems is necessary for watershed management. Alternative techniques for land treatment are determined. In order to come up with a feasible solution to the aforesaid issue, four stages must be completed for watershed management.
Program:
- Recognition phase.
- Restoration phase.
- Protection phase.
- Improvement phase.
Recognition Phase:
Mouthparts with Sponge-like Functions (e.g. Housefly)
Gerbera's Diseases and Infestations.
There are many ways viruses can spread naturally. It necessitates that you go through the proper motions:
- Acknowledgement of a problem
- An examination of the problem's root source and its effect.
- Alternative approaches to issue solving are being developed.
Various surveys, such as soil, land capabilities, agronomic, forest, engineering, and socioeconomic surveys, are used to gather the information needed. This data provides a foundation for resolving watershed issues, setting priorities for land remediation efforts, and identifying the root causes and consequences of environmental and human health issues.
Restoration Phase:
Basically, there are two steps in the restoration phase:
- Identification and selection of the most effective solution to difficulties
- Incorporation of this solution into the land
Priority attention was given to the most important areas first. This is followed by the use of appropriate biological and technical measures to all types of soils.
Protection Phase:
During this stage, the watershed's overall health and functionality are monitored and maintained. A watershed's condition determines what kinds of threats need to be guarded against.
Improvement phase:
During this stage, the entire watershed is being improved and all land is being covered. Agricultural, forestry management and production are given consideration, along with forage production, pasture management, as well as social and economic factors, in order to meet watershed management goals.
Depending on the severity, health, family planning, livestock and poultry improvement, etc. are taken into the account.
Importance of Watershed Management
- The water table is replenished as a result.
- Restoration of soil fertility and conservation of soil
- Drinking and other human needs are restored as a result.
- It aids in the fight against global warming and encourages sustainable farming.
- Conserves a region's biodiversity and, when properly managed, can help restore it.
Concepts of Watershed Management
A lot of attention has been given to air, land, and water pollution in the past. Most efforts have caused in a decrease in pollutant emissions into the air, water and landfills sites.
We still face ongoing issues with the nonpoint sources of pollution and habitat destruction in the water bodies. As a whole, these issues are responsible for the majority of water quality issues.
Nonpoint contamination and habitat deprivation tend to fall under the scope of a wide variety of programs. In order to find a solution to these remaining issues, managements must work together to understand the relationships between environmental components and the required actions to achieve ecosystem integrity.
Practical Example of Watershed management
The technique to save soil and water, to boost the production of biomass compounds is known as watershed management. Columbia River Watershed, Pacific Ocean Watershed, and the Sacramento River Watershed are some popular examples of watershed management
Recent Trends in Watershed Management
As a result of the over-exploitation of natural resources, such as depletion of water supplies, loss of biodiversity, and the development of a wide range of wastes, we must address these challenges on a priority basis.
Water logging and salinization, soil illness, nutrient imbalances, and other second-generation problems have all been linked to increased agricultural production in irrigated locations. There are several factors at play when it comes to ensuring that the expanding requirements of humans and animals for food, fibre, fodder, timber and fuel are met through the efficient use of the land, water and vegetation resources available.
With regard to rainwater management for long-term productivity, efficient water collection technologies and groundwater exploitation are explored. There is an extensive discussion of alternative land-use strategies for reducing land degradation and maximizing economic returns.
Latest Research on Watershed Management
The use of a variety of biological and technical methods, as well as administrative controls, is at the heart of integrated watershed management. The research examines the effects of biological works in the Grdelica Gorge and Vranjska Valley as part of integrated watershed management.
In the second half of the twentieth century, a great deal of work was done to prevent erosion. Ecosystem-based strategies have resulted in a trend of connecting the land surface to vegetation cover, which played important role in preventing erosion.
I hope the blog provides you with in-depth knowledge of Watershed Management and its associated features.
Please feel free to like, share and comment.
Admin, gcelab.com Please see our Pillar Post to know why we founded gcelab.com.
Read More:

Pooja
Founder at gcelab.com, Pooja is an Entrepreneur unlocking human potential. Working in the Principles of Lean Start-up, Pooja believes in Transparency and User Happiness the most. Pooja’s background in teaching gives her a sophisticated grasp on even the most tedious aspect of course building. She is passionate about people who believe that good is not enough.
Previous Post
Project Management and Its Key Features
Next Post


